HashSet - 순서x, ,중복x
규칙
1. Set 인터페이스를 구현한 대표적인 컬렉션 클래스
2. 순서를 유지하려면, LinkedList 사용하면 된다.
3. HashSet은 객체를 저장하기전에 기존에 같은 객체가 있는지 확인필요 ( 중복 허용 x 때문에 )
4. boolean add(Object o)는 저장할 객체의 equals()와 hashCode()를 호출한다.
ㄴ 그래서 equals()와 hashCode()를 오버라이딩이 되어있어야함. ( 없으면 HashSet이 제대로 동작x )
HashSet 주요메서드
| 설명 | 코드 | |
| 1 | 기본생성자 | HashSet() |
| 2 | 생성자 | HashSet(Collection c) |
| 3 | 초기용량 셋팅 | HashSet(int initialCapacity) |
| 4 | 언제용량늘릴지? (ex. loadFactor = 0.8 이면, 80%차면 x2배 늘린다) |
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) |
| 설명 | 코드 | |
| 1 | 추가 | boolean add(Object o) boolean addAll(Collection c) (합집합) |
| 2 | 삭제 | boolean remove(Object o) boolean removeaAll(Collection c) (교집합) |
| 3 | 모두삭제 | void clear() |
| 4 | 조건부삭제 ( 매개변수에있는 Collection만 남기고, 모두삭제 ) (차집합) |
boolean retainAll(Collection c) |
| 설명 | 코드 | |
| 1 | Set에 매개변수 Object를 포함하는지? | boolean contains(Object o) |
| 2 | Set에 Collection에 담긴 여러객체를 포함하는지? |
boolean containAll(Collection c) |
| 3 | 요소읽기 | Iterator iterator() |
| 설명 | 코드 | |
| 1 | 비어있는지? | boolean isEmpty() |
| 2 | 저장된 객체수는? | int size() |
| 3 | Set에 저장된 객체를 객체배열로 반환 | Object[] toArray() Object[] toArray(Object[] a) |
예시 1
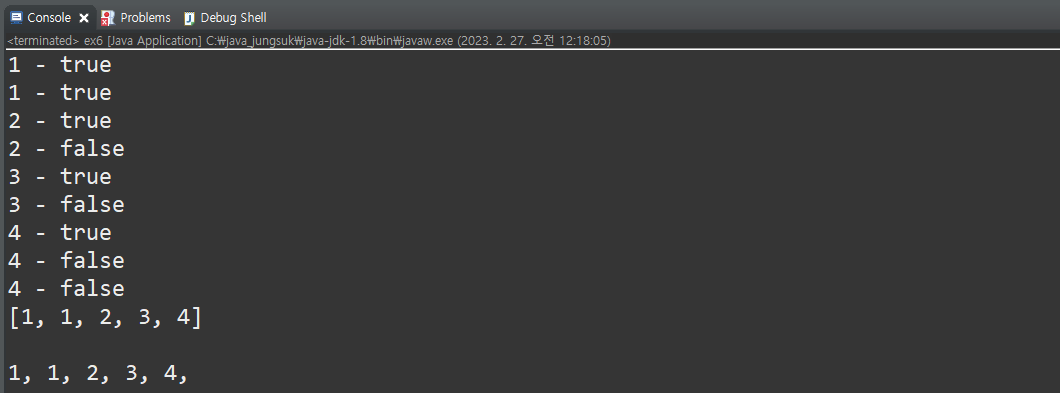
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] objArr = {new Integer(1),"1","2","2","3","3","4","4","4"};
Set set = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; i < objArr.length; i++) { // 중복 값은 저장 false
System.out.println(objArr[i] + " - " + set.add(objArr[i]));
}
System.out.println(set); // 1이 두번 나온 이유는 하나는 정수, 하나는 문자열
System.out.println();
Iterator it = set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Object obj = it.next();
System.out.print(obj + ", ");
}
예시 2
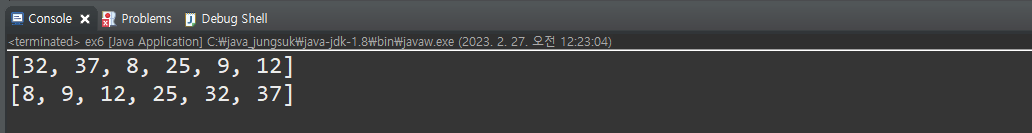
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; set.size() < 6; i++) {
int num = (int)(Math.random() * 45) + 1;
set.add(num);
}
System.out.println(set);
// 순서유지를 위해 LinkedList 사용
List list = new LinkedList(set);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
예시 3
public class ex6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
set.add("abc");
set.add("abc");
set.add(new Person("David",10));
set.add(new Person("David",10));
set.add(new Person("David",10));
System.out.println(set);
// HashSet 사용시 equals()와 HashCode()를 오버라이딩 해야 올바르게 동작함(필수)
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person() {};
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + " : " + age;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (!(obj instanceof Person)) return false;
Person p = (Person) obj;
return this.name.equals(p.name) && this.age==p.age;
}
}
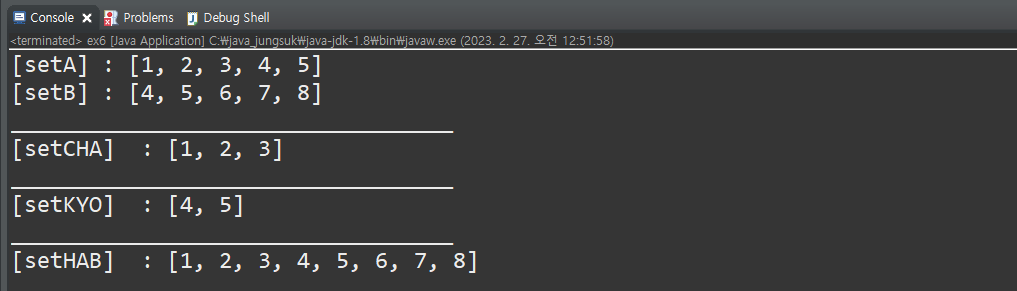
예시 4
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet setA = new HashSet();
HashSet setB = new HashSet();
HashSet setHAB = new HashSet();
HashSet setKYO = new HashSet();
HashSet setCHA = new HashSet();
setA.add("1"); setA.add("2"); setA.add("3");
setA.add("4"); setA.add("5");
System.out.println("[setA] : " + setA);
setB.add("4"); setB.add("5"); setB.add("6");
setB.add("7"); setB.add("8");
System.out.println("[setB] : " + setB);
System.out.println("__________________________________");
Iterator it = setA.iterator();
System.out.print("[setCHA] : ");
while(it.hasNext()) {
Object tmp = it.next();
if(!setB.contains(tmp)) // tmp의 객체중 setB의 객체에 포함되지 않는 것
setCHA.add(tmp);
}
System.out.print(setCHA);
System.out.println("\n__________________________________");
it = setB.iterator();
System.out.print("[setKYO] : ");
while(it.hasNext()) {
Object tmp = it.next();
if(setA.contains(tmp)) // tmp의 객체중 SetA의 객체에 포함되는 것
setKYO.add(tmp);
}
System.out.print(setKYO);
System.out.println("\n__________________________________");
System.out.print("[setHAB] : ");
it = setA.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
setHAB.add(it.next());
}
it = setB.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
setHAB.add(it.next());
}
System.out.print(setHAB);
}
TreeSet - 순서x, 정렬x
규칙
범위 검색과 정렬에 유리한 컬렉션 클래스 ( form ~ to)
HashSet보다 데이터 추가, 삭제에 시간이 더걸림
이진 탐색 트리(binary search tree)로 구현.
이진 트리는 모든 노드가 0~2개의 하위노드를 가지고 있음.
}
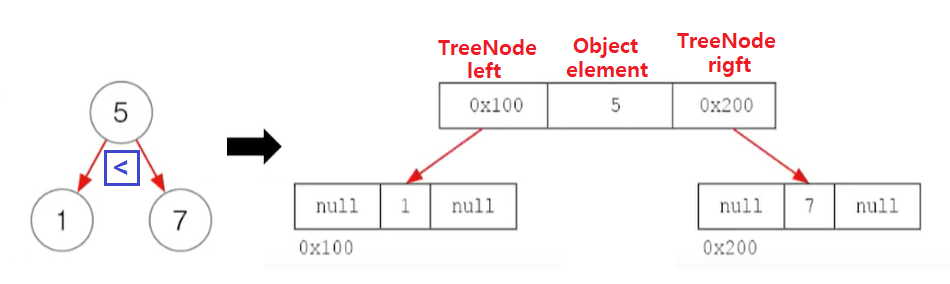
class TreeNode{
TreeNode left; //왼쪽 자식노드
Object element; //저장할 객체
TreeNode right; //오른쪽 자식노드
}이진 탐색 트리(binary search tree)
부모보다 작은 값은 왼쪽, 큰 값은 오른쪽에 저장
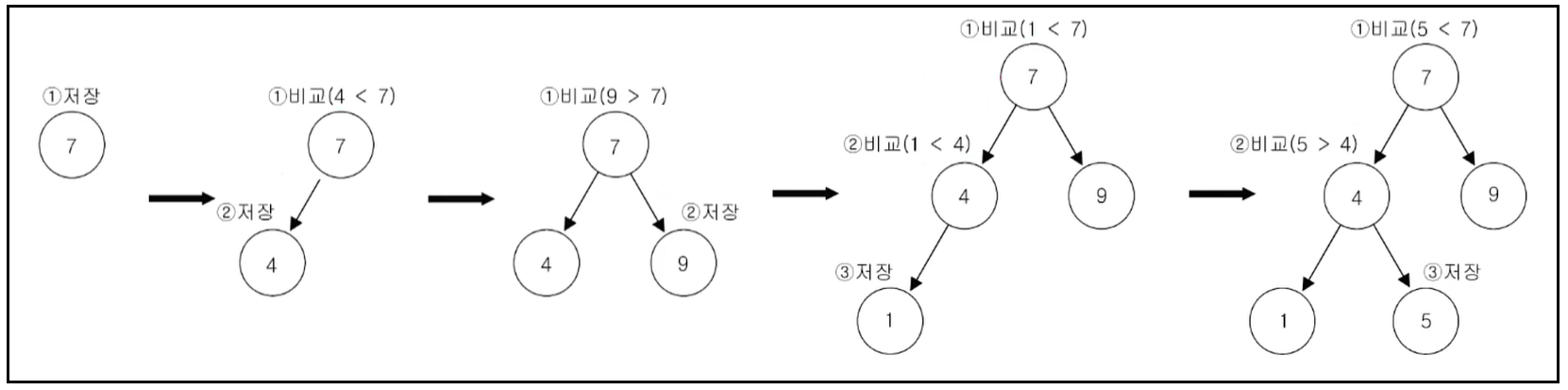
데이터가 많아질수록 추가, 삭제에 시간이 더걸림( 비교횟수 증가)
데이터 저장시 시간이 더걸리는 과정
TreeSet 주요메서드와 메서드
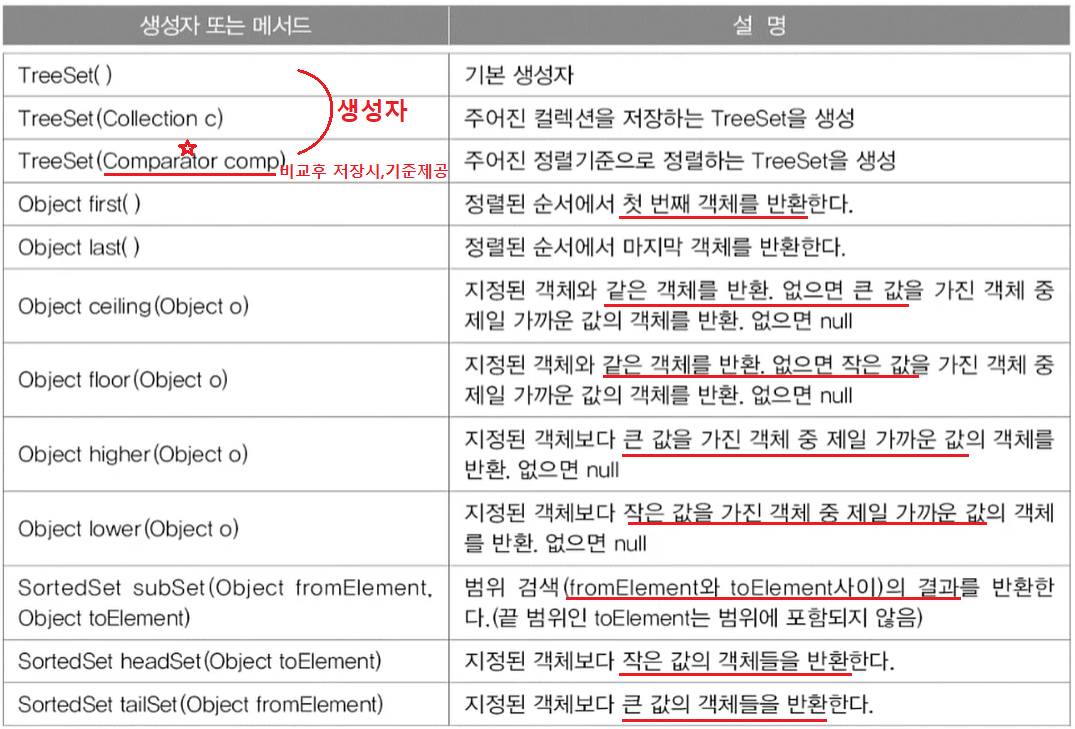
★ TreeSet에 저장할 객체가 Comparable을 구현하여 가지고 있던지,★
TreeSet이 Comparator를 구현하여 정렬기준을 가지고 있어야 한다.
예시 1
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new TreeSet();
for (int i = 0; set.size() < 6; i++) {
int num = (int)(Math.random() * 45 ) + 1;
set.add(num);
}
System.out.println(set);
}
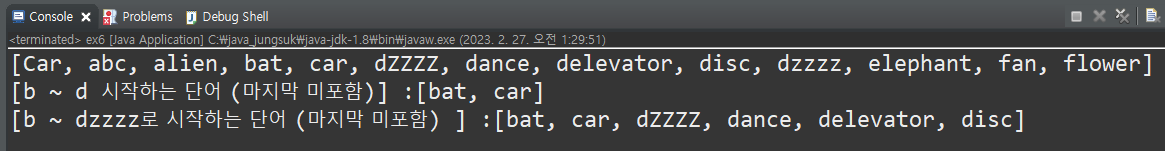
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet set = new TreeSet();
String from = "b";
String to = "d";;
set.add("abc"); set.add("alien"); set.add("bat"); set.add("car");
set.add("Car"); set.add("disc"); set.add("dance"); set.add("dZZZZ");
set.add("dzzzz"); set.add("elephant"); set.add("delevator"); set.add("fan");
set.add("flower");
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println("[b ~ d 시작하는 단어 (마지막 미포함)] :" + set.subSet(from, to));
System.out.println("[b ~ dzzzz로 시작하는 단어 (마지막 미포함) ] :" + set.subSet(from, "dzzzz")); // b ~ bzzzz 로시작하는단어
}
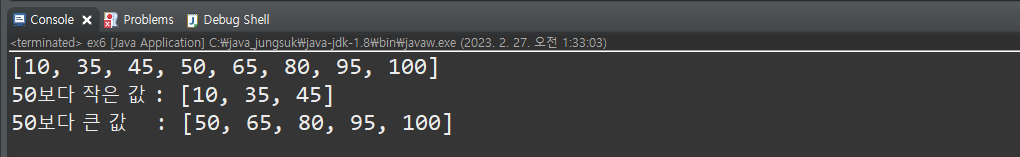
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet set = new TreeSet();
int[] score = {80, 95, 50, 35, 45, 65, 10, 100};
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
set.add(score[i]);
}
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println("50보다 작은 값 : " + set.headSet(50));
System.out.println("50보다 큰 값 : " + set.tailSet(50));
}
트리순회 (tree taversal)
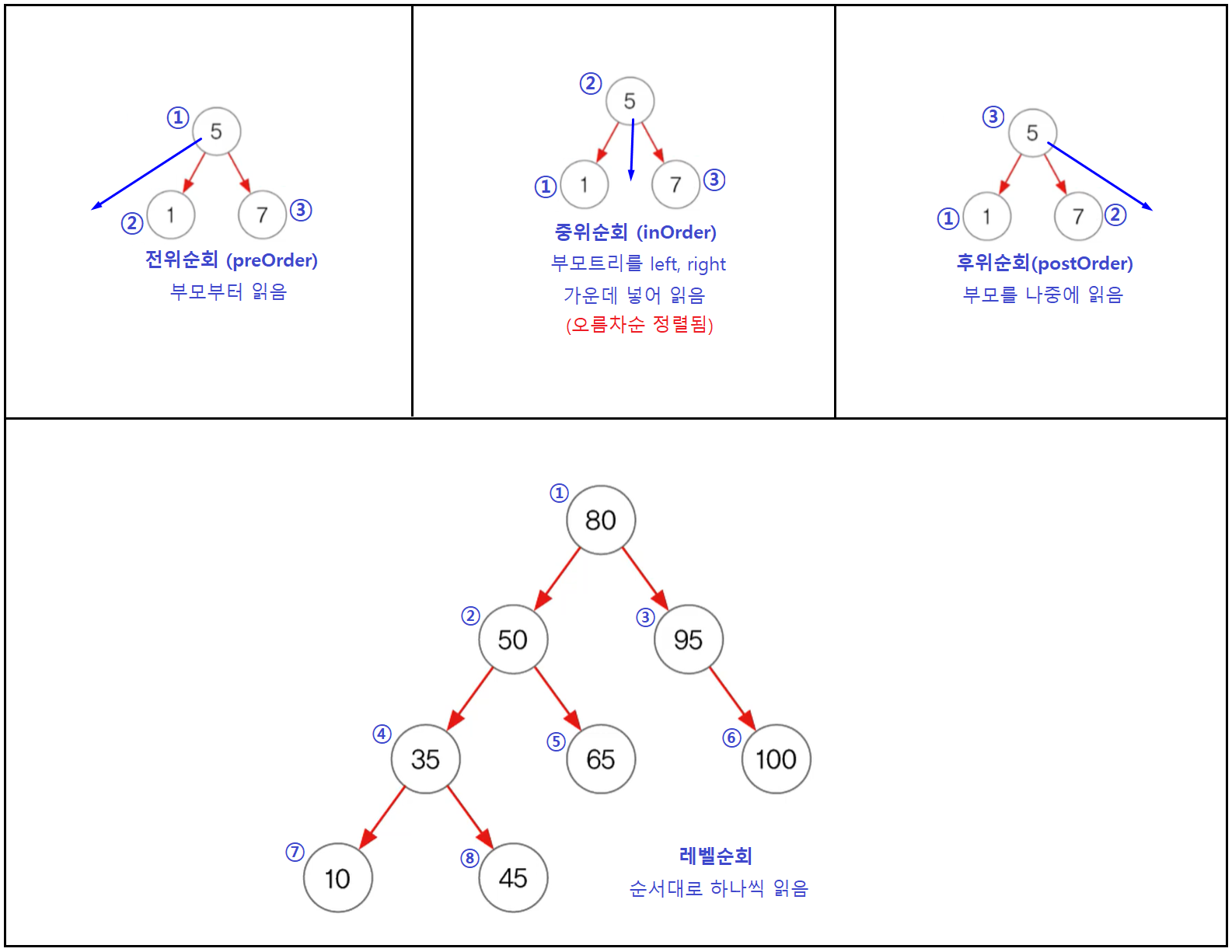
출처 : 남궁성의 정석코딩
'Java의 정석' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 12장. 제네릭스(Generics), 타입 변수,Iterator<E>, 제약 (0) | 2023.02.17 |
|---|---|
| 11장. 컬렉션 ( HashMap, Hashtable, Collections클래스, 정리 ) (1) | 2023.02.16 |
| 11장.Arrays클래스, 검색, Comparator, Comparable 정렬 (0) | 2023.02.14 |
| 11장. 컬렉션( Iterator, ListIterator, Enumeration 인터페이스) (0) | 2023.02.14 |
| 11장. 컬렉션( ArrayList, LinkedList, Stack, Queue인터페이스 ) (0) | 2023.02.13 |